Can Manic Depression Be Cured? Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Recovery Explained

Hey there. If you or a loved one is struggling with mood swings, you probably have one big question. Can manic depression be cured? Dealing with these intense highs and lows feels exhausting. You want answers that actually help you feel better.
I am a board-certified doctor here to help you navigate this journey. This condition is now widely known as bipolar disorder. While the word ‘cure’ is tricky in medicine, the news is actually very good. You can lead a stable, happy, and fulfilling life.
In this guide, we will look at symptoms, triggers, and the latest treatments. We will also explore what real recovery looks like. Let’s dive into the facts so you can take control of your mental health today.
What Is Manic Depression (Bipolar Disorder)?
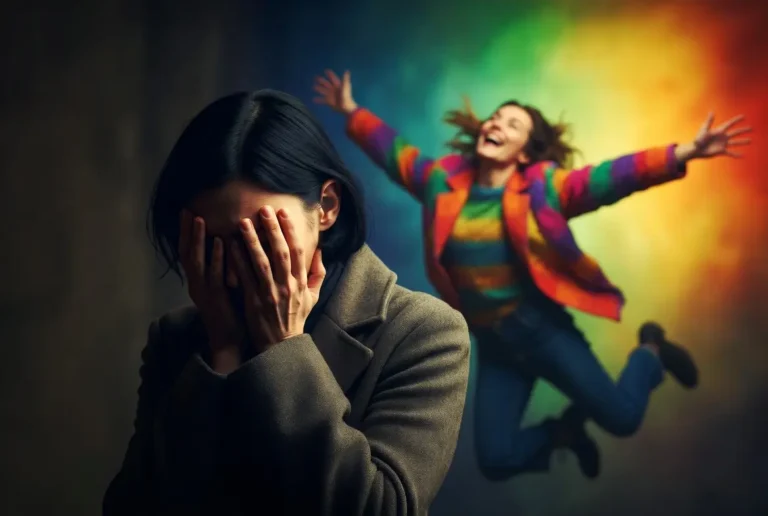
Manic depression is an older medical term. Today, doctors call it bipolar disorder. It is a brain disorder that causes unusual shifts in mood. These are not your typical ups and downs. Instead, they are extreme.
These shifts affect energy and activity levels. They also impact your ability to carry out daily tasks. Furthermore, these episodes can last for days or weeks. Some people feel very “up” or irritable. Others feel very “down” or hopeless.
What Is the Manic Stage of Depression?
The “manic stage” is a period of high energy. You might feel invincible. Specifically, mania involves a decreased need for sleep. You may feel like your thoughts are racing.
There is also a milder version called hypomania. Hypomania does not usually require hospitalization. However, it still feels different from your normal self. In contrast, major depressive disorder lacks these high periods. That is the primary difference.
What Causes Bipolar Disorder?
Scientists are still searching for one single cause. However, we know it is a combination of factors. It is a complex puzzle of nature and nurture.
What Causes Bipolar Disorder in the Brain?
We look at what causes bipolar disorder in the brain through imaging. There are structural differences in the prefrontal cortex. This area controls logic and emotions.
Neurotransmitters also play a huge role. These include dopamine and serotonin. During mania, dopamine levels may be too high. In contrast, they may drop during depression. Circadian rhythm dysregulation is another factor. Your internal body clock is often out of sync.
What Triggers Mania?
Knowing what triggers mania can help you stay stable. Stress is a major culprit. Even “good” stress, like a promotion, can trigger it.
- Sleep Deprivation: Just one missed night can cause an episode.
- Substance Use: Alcohol and drugs destabilize the brain.
- Antidepressants: Sometimes, these meds can “flip” a person into mania.
- Life Events: Grief or major changes are common triggers.
How Long Does Mania Last?
The duration of a manic episode isn’t a “one size fits all” timeline. While clinical definitions provide a baseline, the actual experience can range from a brief, intense burst to a grueling marathon that lasts months.
The Clinical Benchmarks
To be medically classified as a manic episode, symptoms must persist for at least seven consecutive days, or be severe enough to require immediate hospitalization. Hypomania, the less severe but still distinct cousin of mania, typically lasts at least four consecutive days.
Factors Influencing Duration
If left untreated, a manic episode can last anywhere from three to six months. However, several factors determine how long the “high” remains:
- Treatment Intervention: This is the most significant variable. Mood stabilizers and antipsychotics can often “break” an episode within weeks, significantly shortening the cycle.
- Rapid Cycling: Some individuals experience “rapid cycling,” where they move through four or more episodes of mania or depression within a single year.
- Mixed Features: In some cases, symptoms of mania and depression occur simultaneously. These “mixed episodes” can sometimes last longer and are often more difficult to treat.
- Substance Use: Stimulants, caffeine, or alcohol can prolong an episode or increase its intensity, making the “come down” much harder.
The Importance of Early Intervention
The goal of treatment isn’t just to stop the current high, but to stabilize the brain’s chemistry to prevent the inevitable “crash.” When mania goes on too long, it exhausts the body’s resources. The longer and higher the manic peak, the deeper and more debilitating the resulting depressive trough tends to be. By intervening early—usually through a combination of medication and routine-based therapy—you can “level out” the peaks and valleys, leading to a much faster recovery.
Note: If you or someone you know is experiencing a manic episode that includes psychosis (hallucinations or delusions) or thoughts of self-harm, seek emergency medical care immediately.
Manic Depression Symptoms
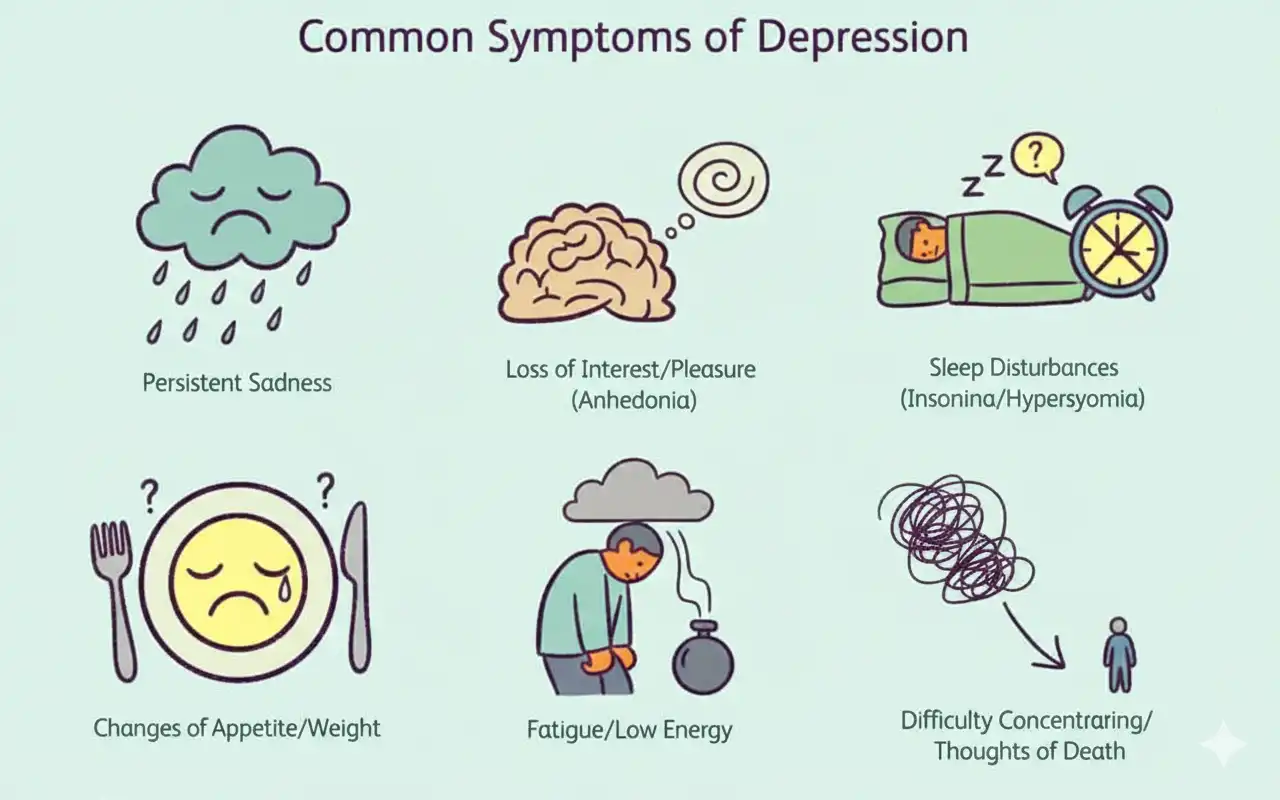
Recognizing manic depression symptoms is the first step toward help. Symptoms fall into two distinct categories. These are the “highs” and the “lows.”
Common Manic Depression Symptoms
During mania, you may feel “jumpy” or wired. You might talk very fast about many different things. Often, people have a very high appetite for risk. For instance, they might spend too much money.
During the depressive phase, you feel very tired. You may have trouble concentrating. Most noteworthy is the feeling of emptiness. You might lose interest in activities you once loved.
Bipolar Disorder Symptoms in Females
Research shows that biological sex plays a role. Bipolar disorder symptoms in females often involve more depression. Women are also more likely to experience rapid cycling. This means having four or more episodes in a year.
Hormonal changes can trigger symptoms as well. This includes the postpartum period or menopause. Also, women have higher rates of co-occurring conditions. These include thyroid issues and anxiety.
How a Person With Bipolar Disorder Thinks
Understanding how a person with bipolar disorder thinks helps build empathy. The brain functions differently during different phases. It is not a choice or a character flaw. It is biology.
Thought Patterns During Mania
During mania, the brain’s “brakes” fail. You might experience grandiosity. This is a fancy word for feeling over-important. You may believe you have special powers.
Racing thoughts are also very common. One idea leads to another very quickly. Consequently, it is hard to stay focused on one task. This leads to impulsive decisions that seem logical at the time.
Thought Patterns During Depression
In the low phase, thoughts become “sticky” and dark. There is a strong negative bias. You might remember only your mistakes. Cognitive slowing also occurs.
It feels like thinking through molasses. Simple choices feel impossible. Most importantly, some may face suicidal ideation. If this happens, please seek emergency help immediately. You are not alone.
Bipolar Disorder Test & Diagnosis
If you suspect you have this, you need a professional. You cannot diagnose yourself at home. But you can use screening tools.
Online Bipolar Disorder Tests (Screening Only)
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) is a common bipolar disorder test. It asks about your history of “highs.” If you score high, it does not mean you have bipolar.
It simply means you should see a doctor. Online tests are just the first step. They are not a clinical diagnosis. Use them as a conversation starter with your MD.
How Bipolar Disorder Is Diagnosed Clinically
Doctors use the DSM-5 criteria. We look for a pattern of symptoms over time. We also rule out other causes. For instance, thyroid problems can mimic mood swings.
We will ask about your family history. We also look at your medication history. This process ensures you get the right treatment. Misdiagnosis can lead to the wrong meds.
Can You Recover From Manic Depression?
This is the question I hear most in my clinic. People want to know if life gets better. The answer is a resounding yes. But we must be honest about the definitions.
Can Manic Depression Be Cured?
Technically, there is no permanent cure. You cannot take a pill for a month and be rid of it forever. However, this does not mean you are “sick” forever.
Many chronic conditions have no cure. Take Type 1 Diabetes as an example. You manage it, but you don’t “cure” it. Bipolar disorder is very similar. Therefore, we focus on management and thriving.
What Recovery Really Means in Bipolar Disorder
Recovery is a journey, not a destination. It means achieving symptom remission. This is when your symptoms go away for long periods.
It also means functional recovery. This is your ability to work and have relationships. With the right tools, you can achieve both. Relapse prevention is the key to staying recovered.
Most Effective Treatment for Bipolar Disorder
Finding the most effective treatment for bipolar disorder takes time. It is often a “trial and adjustment” process. Work closely with your psychiatrist.
Medications (First-Line)
Medication is the foundation of treatment. We use different classes of drugs.
| Class | Examples | Purpose |
| Mood Stabilizers | Lithium, Valproate | Prevents highs and lows |
| Antipsychotics | Quetiapine, Risperidone | Controls acute mania |
| Anticonvulsants | Lamotrigine | Mostly prevents depression |
Lithium remains the “gold standard.” It has the strongest evidence for preventing suicide. Always take these as prescribed. Stopping suddenly can cause a severe relapse.
Psychotherapy
Medicine fixes the biology. Therapy fixes the lifestyle. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is excellent. It helps you catch “red flag” thoughts early.
Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT) is also vital. It focuses on your daily routines. Specifically, it helps you stabilize your sleep-wake cycles.
Lifestyle Interventions
Do not underestimate the power of habits. Regular exercise helps regulate mood. Nutrition is also important. Some studies suggest Omega-3 fatty acids help.
However, be careful with supplements. Some can interact with your meds. Always talk to your doctor first. Finally, avoid caffeine and nicotine as they disrupt sleep.
How to Cure Severe Depression & Anxiety — What Actually Works
Many people search for a cure for clinical depression. They want to know how to cure severe depression quickly. While there is no “instant fix,” there are powerful tools.
Is There an Instant Cure for Depression?
No, there is no instant cure for depression. Beware of anyone promising one. Healing the brain takes time and consistency. However, some treatments work faster than others.
For example, Ketamine therapy can work in hours. But it is not a “cure.” You usually need repeated sessions. It is a tool for crisis management.
Evidence-Based Treatments for Depression & Anxiety
Standard treatments are very effective. SSRIs and SNRIs help many people. Therapy provides long-term coping skills.
For severe cases, we use advanced options. These include Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is also very safe today. These help when meds do not work.
Why Many Serious Diseases Don’t Have “Cures” (Yet)
It can be frustrating to hear “no cure.” You might wonder about other conditions too. Why is medicine so slow?
Why There Is No Instant Cure in Modern Medicine
Human biology is incredibly complex. Diseases like cancer or bipolar disorder involve many genes. They are not caused by a single germ.
The environment also plays a role. Therefore, a “one-size-fits-all” cure is hard to find. We are moving toward “personalized medicine” instead. We treat your specific genetic makeup.
Current Medical Reality for These Conditions
Here is a quick look at other chronic conditions.
| Condition | Cure Status | Management Approach |
| Thrombocytopenia | No universal cure | Treat the underlying cause |
| Myelofibrosis | No cure (except transplant) | Symptom management |
| Mesothelioma | No cure | Surgery and oncology care |
| Huntington’s Disease | No cure | Supportive and palliative care |
| Hepatitis C | Curable | Modern antiviral meds |
| Polycythemia | No cure | Phlebotomy (blood thinning) |
| Vitiligo | No cure | Light therapy/Repigmentation |
| Cholesterol | No “cure” | Statins and diet changes |
As you can see, most chronic things are “managed.” This is the reality of modern health. But management leads to a long life.
When to See a Doctor Immediately
Sometimes, you cannot wait for an appointment. Mental health crises are medical emergencies.
See a doctor if you feel “out of control.” If you haven’t slept in three days, go to the ER. This is a sign of acute mania. Also, seek help if you have thoughts of self-harm.
Watch for severe medication side effects. These include rashes or extreme tremors. Your safety is the top priority. Never feel ashamed to ask for help.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can bipolar disorder go away on its own?
No, it rarely goes away without help. Untreated bipolar often gets worse over time. Episodes may become more frequent.
Is bipolar worse with age?
It can be if left untreated. Chronic stress on the brain causes damage. However, with treatment, many people get more stable as they age.
Can lifestyle changes replace medication?
For most people, no. Lifestyle changes are “add-ons.” They make the medicine work better. But they usually cannot replace it entirely.
Are supplements safe for bipolar disorder?
Some are, but many are not. For instance, St. John’s Wort can trigger mania. Always check with your psychiatrist first.
Final Thoughts on Recovery
So, can you recover from manic depression? Yes, you absolutely can. You might have to live with the diagnosis. But you do not have to live with the chaos.
Start by finding a doctor you trust. Be patient with the process. Use the transition words of your life to move forward. First, get diagnosed. Second, start treatment. Finally, enjoy your stability.
Can manic depression be cured? Perhaps not in the traditional sense. But a life of peace and joy is within your reach. Reach out today and take that first step.
Medical Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only. It does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions regarding a medical condition.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get mental health tips, updates, and resources delivered to your inbox.