Bipolar Disorder Statistics, Facts & Treatment (2026 Guide)
Hey there. Are you looking for the truth behind the numbers? You are not alone in this search. Many people feel overwhelmed by a mental health diagnosis. As a doctor, I believe that data provides clarity. We use bipolar disorder statistics to build better care systems. These numbers help us understand the global and local impact. In this guide, we will explore the latest updates for 2026. We will look at who is affected and why. Furthermore, we will see how modern treatment changes the outcome. Understanding these facts is the first step toward stability. Let’s dive into the real data together right now.
Global Bipolar Disorder Statistics (2026 Update)
Bipolar disorder is a major global health concern. Consequently, it ranks as a top cause of disability. Experts estimate that nearly 46 to 54 million people live with it. This represents about 1% to 2.4% of the global population.
Specifically, global prevalence bipolar disorder statistics show steady growth. This is often due to better screening tools. According to WHO bipolar disorder statistics, it is the sixth leading cause of disability. It impacts people across all cultures and income levels.
In addition, many cases remain hidden in low-income regions. This is because mental health resources are scarce. Therefore, the actual worldwide burden might be higher. Developed nations often report more cases due to better access. However, the biological rate stays fairly consistent everywhere.
Bipolar Disorder Statistics by Country
Looking at specific nations helps us see local trends. First of all, the United States has high reporting rates. We have some of the best screening systems in place.
According to NIMH bipolar disorder statistics, 2.8% of US adults are affected. This equals roughly 7 million Americans. Other countries show slightly different numbers. For example, bipolar disorder statistics Canada indicate a 2.2% prevalence. Australia reports around 1.3% for its population.
In the Philippines, statistics are harder to track. Stigma often prevents people from seeking help there. However, awareness campaigns are currently growing. Consequently, more people are receiving proper diagnoses today.
Prevalence Rates by Country (2026 Estimates)
| Country | Estimated Prevalence | Primary Data Source |
| United States | 2.8% | NIMH / SAMHSA |
| Canada | 2.2% – 3.4% | CMHA |
| Australia | 1.3% – 1.8% | AIHW |
| United Kingdom | 1.0% – 2.0% | Bipolar UK |
| New Zealand | 2.1% | Ministry of Health |
| Philippines | 1.0% (estimated) | WHO Country Profile |
Bipolar Disorder Statistics Over Time (2021–2026)
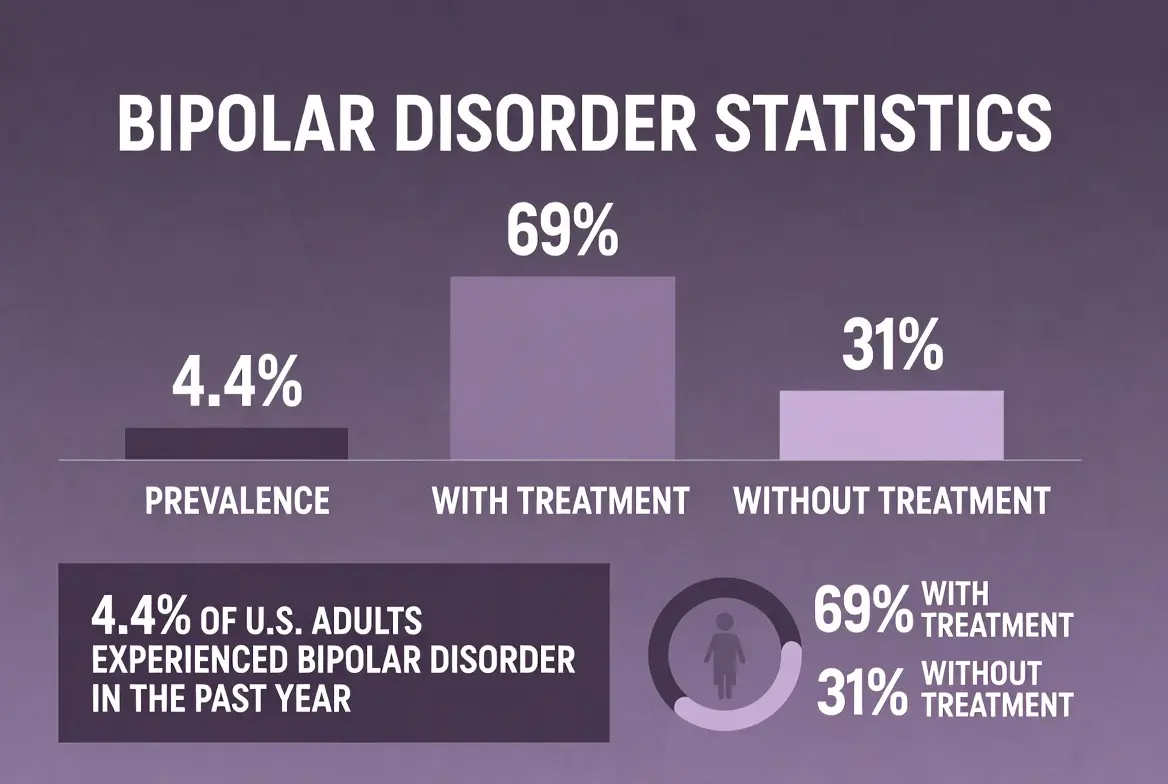
Data has shifted significantly over the last few years. For instance, bipolar disorder statistics 2021 showed a pandemic spike. Stress and isolation triggered many new episodes.
Later, bipolar disorder statistics 2023 reflected better digital care. Telehealth made it easier to see a psychiatrist. Now, bipolar disorder statistics 2026 show a focus on early intervention. We are catching symptoms in teens much faster.
Moreover, the “diagnostic gap” is slowly closing. In the past, people waited 10 years for a diagnosis. Consequently, they suffered without the right meds. Today, that wait time is decreasing in many areas.
Prevalence, Gender & Age-Based Statistics
Who is most likely to have bipolar disorder? Statistics provide a clear demographic profile. First of all, age is a major factor.
The average age of onset is 25 years old. However, symptoms often start in the late teens. Teenage bipolar disorder statistics show about 2.9% of adolescents are affected. This age group also faces the highest impairment.
Regarding gender, the split is nearly equal. Bipolar disorder statistics men vs women show a 1:1 ratio. But the symptoms often differ by sex. For example, women experience more depressive episodes. Men are more likely to face severe mania.
Also, what percentage of people have bipolar 2? Data suggests around 1.1% of adults. Bipolar 1 is slightly more prevalent at 1.5%. Essentially, 1 in every 35 adults lives with this condition.
Bipolar Disorder & Depression Statistics
Many people confuse bipolar with standard depression. In fact, misdiagnosis is a common problem. Depression and bipolar disorder statistics tell a tough story.
About 69% of patients get the wrong diagnosis first. Usually, they are told they have major depression. Consequently, they receive antidepressants alone. This can actually trigger a manic episode.
Furthermore, the suicide risk is much higher here. People with bipolar are 20-30 times more at risk. This is significantly higher than those with unipolar depression. Therefore, getting the right diagnosis is literally a lifesaver.
Psychology, Causes & Risk Factors
What causes this complex brain disorder? Bipolar disorder psychology points to several factors. First and foremost is genetics.
If one parent has it, the risk is 15-30%. If both parents have it, the risk jumps to 75%. This makes it one of the most heritable conditions.
In addition, brain chemistry plays a role. We see imbalances in dopamine and serotonin. Environmental triggers also matter a lot. For example, extreme stress can start the first episode. Childhood trauma is another significant risk factor.
20 Facts & Interesting Statistics About Bipolar Disorder
Looking for quick facts? Here is a breakdown of the most vital data.
Top 10 High-Impact Facts
- Fact 1: It is the 6th leading cause of disability globally.
- Fact 2: Nearly 83% of cases are classified as “severe.”
- Fact 3: It reduces life expectancy by an average of 9 years.
- Fact 4: Over 50% of patients have a substance use issue.
- Fact 5: Creatives are 25% more likely to carry these genes.
- Fact 6: Lithium reduces suicide risk by over 60%.
- Fact 7: Lack of sleep is the #1 trigger for mania.
- Fact 8: Most people see 3-4 doctors before a correct diagnosis.
- Fact 9: Exercise can reduce depressive symptoms by 30%.
- Fact 10: It costs the US economy over $200 billion annually.
More Noteworthy Stats
- Fact 11: 1 in 5 patients will attempt suicide without care.
- Fact 12: Bipolar 2 involves more frequent “lows.”
- Fact 13: Rapid cycling affects about 15% of patients.
- Fact 14: Most first episodes happen between ages 18-24.
- Fact 15: Women have higher rates of thyroid issues with bipolar.
- Fact 16: 90% of those with the condition are satisfied with meds.
- Fact 17: Routine is the best non-drug mood stabilizer.
- Fact 18: Only 25% of people get a diagnosis within a year.
- Fact 19: It affects all ethnic groups at similar rates.
- Fact 20: Anxiety co-occurs in 75% of bipolar cases.
Diagnosis & Self-Assessment Statistics
Early detection changes everything. Consequently, we push for regular screening. A bipolar disorder test is often the first step.
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) is very popular. It helps doctors spot manic tendencies. However, these tests are only for screening. You need a full clinical interview for a diagnosis.
Currently, about 56% of people remain undiagnosed. This is a major public health gap. Therefore, we are training more primary care doctors. We want them to spot the signs early.
Treatment Statistics & Effectiveness
Does treatment actually work? The numbers say yes. Treatment for bipolar disorder is highly effective today.
First of all, bipolar disorder medications are the foundation. Lithium and Valproate are common mood stabilizers. In fact, 75% of patients improve on these.
In addition, psychotherapy for bipolar disorder adds value. Specifically, CBT reduces relapse rates by 40%. Therapy for bipolar disorder helps you manage stress. Combined, these treatments offer the best chance for stability.
Furthermore, bipolar disorder counseling helps family members. It reduces the “expressed emotion” at home. This leads to a calmer environment for recovery.
Facilities, Clinics & Support Resources
Where should you go for help? There are many options available.
A specialized bipolar disorder clinic is ideal. They have experts who only treat mood disorders. For crises, bipolar disorder inpatient treatment is necessary. This provides 24/7 safety and care.
In addition, use bipolar disorder support groups. Organizations like NAMI and DBSA are excellent. They offer free bipolar disorder resources for everyone. These groups remind you that you are not alone.
Living With Bipolar Disorder: Life Outcomes
Can a person with bipolar live a normal life? This is the most important question. The answer is a loud yes.
With treatment, 60% of patients work full-time. Many are leaders in their fields. Stability depends on a few key factors. For instance, how many hours should bipolar sleep? Most need 7 to 9 hours of quality rest. Sleep is the “anchor” for your brain. If you sleep well, your risk of mania drops. Consequently, you can maintain a steady, happy life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are some statistics about bipolar disorder in 2026?
Nearly 2.8% of US adults live with bipolar disorder. Globally, the number is around 46 to 50 million. Most people are diagnosed in their early 20s.
What are the statistics for bipolar disorder and suicide?
The risk is 20 to 30 times higher than average. However, consistent treatment significantly reduces this risk. Suicide prevention is a key goal of therapy.
What are the statistics of bipolar disorder in teenagers?
About 2.9% of teens aged 13-18 have the condition. It often presents with severe impairment in school. Early intervention leads to much better adult outcomes.
Final Summary of Bipolar Disorder Statistics
In conclusion, bipolar disorder statistics show a clear picture. The condition is common and often severe. However, it is also very treatable.
The numbers for 2026 show that we are making progress. We are diagnosing people faster than ever before. Consequently, more people are finding stability.
You are not just a data point in a study. You are a person with a bright future. Therefore, use these facts to empower your journey. Reach out to a professional today for help. Recovery is not just a hope—it is a statistical reality for most.
Medical Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes. It does not replace clinical advice. Always consult a doctor for mental health concerns.
Authoritative References
1. National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
2. World Health Organization (WHO)
3. StatPearls – National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)
4. Global Burden of Disease Study (General Psychiatry / The Lancet)
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get mental health tips, updates, and resources delivered to your inbox.







