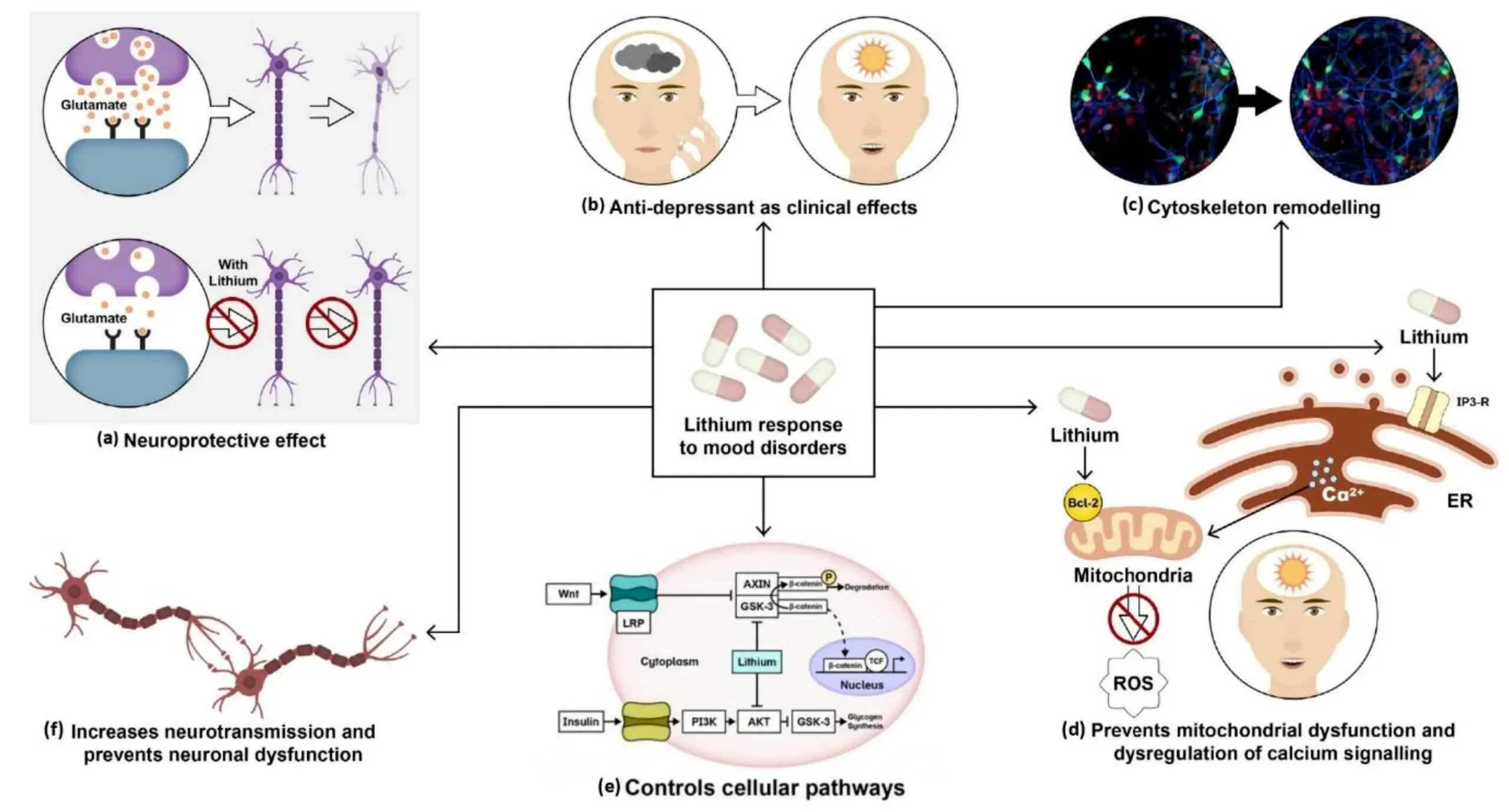
Bipolar Medication Costs Without Insurance: Options, Prices & Help

Navigating a diagnosis like bipolar disorder is challenging enough without the added weight of financial uncertainty. For the millions of Americans currently living without health insurance, the first question after a diagnosis isn’t just “How do I get better?” but “How much is bipolar medication cost without insurance?”
The fear of high drug costs often acts as a barrier to treatment, leading many to delay care until a crisis occurs. However, the landscape of mental health pricing has shifted significantly. With the rise of generic alternatives, discount programs, and community-based resources, managing bipolar disorder without insurance is more achievable in 2026 than ever before.
This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the costs associated with bipolar care, from psychiatrist visits to monthly prescription totals, and offers actionable strategies to access help even when funds are limited.
How Much Does It Cost to Treat Bipolar Disorder?
If you are paying out-of-pocket, your expenses will be divided into three primary categories: provider fees, medication, and diagnostic monitoring.
Psychiatric Visits
Psychiatrists are medical doctors (MDs) specializing in mental health. Because they handle complex medication management, their fees are generally higher than those of therapists.
- Initial Evaluation: Expect to pay between $250 and $600 for your first visit. This session typically lasts 60–90 minutes and involves a full diagnostic assessment.
- Follow-up Appointments: Once a treatment plan is established, follow-ups (15–30 minutes) usually cost $100 to $300. Initially, these may occur monthly; once stable, they may drop to every 3–6 months.
Laboratory Work and Monitoring
Certain bipolar medications, particularly Lithium and Clozapine, require regular blood tests to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- Lab Fees: Without insurance, a standard blood panel (checking kidney function, thyroid, and drug levels) can cost $50 to $150 per test.
Monthly Cost Estimates
| Service | Low-End (Generic/Clinic) | High-End (Brand/Private) |
| Psychiatry (Initial) | $150 (Community Clinic) | $600+ (Private Practice) |
| Psychiatry (Monthly) | $80 (Telehealth) | $300 (In-person) |
| Medication (Monthly) | $10 – $40 | $500 – $1,200 |
| Lab Work (Per Visit) | $40 | $150+ |
Bipolar Medication Names List: Context for Cost
To understand pricing, you must first know which class of medication you are taking. Bipolar treatment is rarely a “one-pill” solution; most patients utilize a combination of the following:
- Mood Stabilizers: The “gold standard” for preventing mania and depression (e.g., Lithium, Valproic Acid).
- Anticonvulsants: Often used as mood stabilizers (e.g., Lamotrigine, Carbamazepine).
- Atypical Antipsychotics: Used for acute mania and maintenance (e.g., Quetiapine, Olanzapine, Aripiprazole).
- Antidepressants: Sometimes used as adjuncts, though carefully monitored to prevent “switching” into mania (e.g., Sertraline, Fluoxetine).
Cost of Common Bipolar Medications Without Insurance
The following section provides a detailed look at the cash prices for the most frequently prescribed bipolar medications as of 2026.
Lithium Medication Cost Without Insurance
Lithium remains one of the most effective and affordable treatments for bipolar disorder.
- Generic Pricing: The average retail price for a 30-day supply of generic Lithium Carbonate (300mg) is approximately $25 to $40.
- With Discounts: Using tools like GoodRx, you can often find it for as low as $12 to $18.
- Brand Name (Lithobid): Avoid the brand name if possible; it can cost over $1,000 for the same therapeutic effect as the generic.
Lamotrigine Cost Without Insurance (Dose-Specific)
Lamotrigine (Lamictal) is widely used for bipolar depression. Its cost varies slightly based on the dosage required for maintenance.
- Lamotrigine 25 mg/100 mg (Starting/Titration): Usually $15–$30 per month.
- Lamotrigine 200 mg/300 mg (Maintenance): Approximately $30–$60 per month.
- Note: Because Lamotrigine must be “titrated” (started at a very low dose and increased slowly), your first two months may actually be cheaper than your long-term maintenance cost.
Quetiapine Cost Without Insurance
Quetiapine (Seroquel) is an antipsychotic used for both sleep and mood stabilization.
- Generic Pricing: A 30-day supply of 25mg tablets averages $20–$50.
- Higher Doses: For mood stabilization doses (300mg+), the retail price can climb to $100–$250, though coupons frequently bring this down to the $30 range.
Olanzapine Cost Without Insurance
How much does a 30-day supply of olanzapine cost?
- Generic Zyprexa: Retail prices hover around $150–$200 for 5mg or 10mg tablets.
- Discounted Price: With a prescription discount card, the cost often drops to $15–$25 for 30 tablets.
Antidepressants & Mental Health Meds Without Insurance
Many people with bipolar disorder are also prescribed adjunct medications for anxiety or depressive symptoms.
- Zoloft (Sertraline) Cost: Generic Zoloft is incredibly inexpensive, often costing $10 or less for a 30-day supply at pharmacies like Walmart or Costco.
- Antidepressants Online: Many telehealth platforms offer “subscription” models where the cost of the doctor visit and the medication (SSRIs) are bundled for a flat fee of $50–$95 per month.
- Caution: If you have bipolar disorder, never take antidepressants without a mood stabilizer, as this can trigger a manic episode.
Therapy Without Insurance: What Does It Cost?
Talk therapy is a vital component of long-term stability. Without insurance, the standard rate for a private therapist is $100 to $250 per hour.
If this is out of reach, consider:
- Sliding Scale Clinics: These providers adjust their fees based on your income. You may pay as little as $30 to $60 per session.
- Training Clinics: University psychology departments often offer therapy with supervised graduate students for $10 to $20.
- Group Therapy: Often costing $40 to $70 per session, group work provides professional guidance at a fraction of the individual cost.
How to Get Treatment for Bipolar Disorder Without Insurance

If you are currently in a position where you cannot afford the prices listed above, there are several “safety net” systems designed to help.
Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs)
These are community-based organisations that receive government funding to provide care to underserved populations. They offer primary care and mental health services on a sliding fee scale. You can find one near you using the HRSA Find a Health Center tool.
Prescription Assistance Programs (PAPs)
Most major pharmaceutical companies (like AstraZeneca or Janssen) have programs that provide medications for free or nearly free to individuals who meet certain income requirements and lack insurance.
Teaching Hospitals
If you live near a university hospital, they often have “charity care” policies or outpatient clinics run by residents that offer significantly reduced rates for psychiatric evaluations.
Prescription Drug Costs Without Insurance: How to Lower Them
Never pay the “window price” at a pharmacy. Use these three steps to slash your drug costs without insurance:
- Ask for the “Cash Price”: Sometimes a pharmacy’s internal discount price is lower than what a coupon provides.
- Use Discount Cards: GoodRx, SingleCare, and NeedyMeds are essential. Show the coupon on your phone to the pharmacist before they ring you up.
- Choose 90-Day Fills: Ordering a 3-month supply is often 20–30% cheaper than buying three separate 1-month supplies.
Comparing Other High-Cost Medications
It can be frustrating to see the price of mental health meds, but it helps to put them in perspective with other common out-of-pocket costs.
- Cost of Synthroid Without Insurance: ~$50/month (Generic Levothyroxine is ~$10).
- How Much is Ozempic Without Insurance: ~$900–$1,200/month.
- Cost of Suboxone Without Insurance: ~$150–$400/month.
While bipolar medications can be expensive, they are among the most frequently discounted drugs in the U.S. healthcare system, making them far more “negotiable” than high-cost biologics or weight-loss medications.
What Is the 48-Hour Rule for Bipolar People?
The “48-hour rule” is a clinical principle in psychiatric crisis management that emphasizes the narrow window of opportunity for early intervention. It suggests that if a person experiencing the first signs of a manic or depressive “shift” receives medical adjustment within 48 hours of the first symptom change, the likelihood of a full-blown episode requiring hospitalization drops by over 60%.
From a financial perspective, the 48-hour rule is your most powerful cost-saving tool.
- The Cost of Waiting: If symptoms are ignored, they often escalate into a state requiring emergency services. In 2026, the average cost of psychiatric hospitalization without insurance ranges from $1,000 to $2,500 per day. A typical one-week stabilization stay can easily result in a bill exceeding $15,000.
- The Cost of Early Action: An urgent “fit-in” appointment with a psychiatrist may cost $150–$300, and a minor medication adjustment might add only $20 to your monthly pharmacy bill.
By acting within that first 48-hour window, you are essentially spending hundreds today to save tens of thousands tomorrow.
The Breakdown of Generic vs. Brand-Name Costs

When you don’t have insurance, you are essentially a “cash-pay” customer. In this role, your greatest leverage is generic bioequivalence.
Tier 1: Low-Cost Generics (The $10–$50 Range)
Most “foundational” bipolar medications have been off-patent for decades, meaning multiple manufacturers compete to keep prices low.
- Aripiprazole (Generic Abilify): While once expensive, it now often costs as little as $11–$40 per month with a coupon.
- Risperidone (Generic Risperdal): A common antipsychotic that can be found for $8–$20 for a 30-day supply.
- Asenapine (Generic Saphris): A mid-tier generic that typically costs about $75 (an 80% drop from its $500+ retail price).
Tier 2: High-Cost Brand Names (The $1,000+ Range)
If your psychiatrist recommends a “newer” medication, you are likely looking at a drug still under patent protection.
- Vraylar (Cariprazine): With no generic available in 2026, the cash price often sits at $1,300+.
- Caplyta (Lumateperone): Similarly, this can retail for $1,400+.
- The Strategy: If these are prescribed, you must look for Manufacturer Patient Assistance Programs (PAPs). Companies like AbbVie (Vraylar) or Intra-Cellular Therapies (Caplyta) often provide the drug for $0 to uninsured patients who fall below specific income thresholds (usually 400-500% of the Federal Poverty Level).
Hidden Costs: Lab Monitoring and Titration
The “monthly pill cost” isn’t the only expense. Bipolar care involves biological maintenance that can catch the uninsured off guard.
The Lab Fee “Gotcha”
Medications like Lithium and Valproic Acid are effective but require blood monitoring to prevent toxicity.
- Initial Phase: You may need labs every 1–2 weeks until your dose is stable.
- Maintenance Phase: Labs occur every 3–6 months.
- Cost-Saving Tip: Use independent labs like Quest Diagnostics or LabCorp and ask for their “Patient-Authorized” or “Pre-paid” pricing, which can be 50–70% cheaper than labs ordered through a hospital system.
The Titration Price Jump
Drugs like Lamotrigine require a “starter pack” or a slow increase in dosage (titration).
- You might start at 25mg and end at 200mg.
- The Cost Trap: Some pharmacies charge by the “fill,” not the milligram. You may pay $15 for 25mg tablets and then $15 again for 100mg tablets. Always check if a 90-day supply of the final dose is cheaper than multiple 30-day fills of varying doses.
The “Cost Plus” Revolution: A New Way to Buy
Since 2022, “Cost Plus” pharmacies have disrupted the traditional model. Platforms like Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company or Amazon Pharmacy bypass the “middlemen” (Pharmacy Benefit Managers).
- Transparency: They charge the actual cost of the drug + a 15% markup + a small shipping/handling fee.
- Price Comparison: For many bipolar meds, the “Cost Plus” price is lower than the GoodRx price at a local CVS or Walgreens. For example, generic Lurasidone (Latuda) can be hundreds of dollars cheaper on these platforms than at a retail counter.
Strategic Navigation: How to Get Help Now
If you have $0 and no insurance, your path follows a specific hierarchy of resources:
The HRSA Find-a-Clinic Tool
The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) maintains a database of Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs).
- Why they are unique: These clinics must treat you regardless of your ability to pay.
- The Pharmacy Benefit: Most FQHCs have access to 340B Pricing—a federal program that allows them to buy drugs at a massive discount and pass those savings to you. You might get a $200 medication for $5.
Nonprofit Copay Foundations
Organizations like the PAN Foundation or HealthWell Foundation offer specific “Bipolar Disorder Funds.”
- In 2026, these grants can provide up to $4,400 per year to cover the out-of-pocket costs of medications for those who qualify financially.
State Pharmaceutical Assistance Programs (SPAPs)
While often associated with seniors, some states offer pharmaceutical assistance to low-income residents with chronic mental health conditions. Check your state’s Department of Health website for “Prescription Assistance.”
Out-of-Pocket Cost Structure for Bipolar Care

To build an accurate budget, you must account for the three pillars of treatment: professional fees, the medication itself, and mandatory biological monitoring.
Psychiatric Provider Fees
Psychiatrists (MDs or DOs) handle the biological side of bipolar disorder.
- The Diagnostic Intake: Without insurance, an initial 60-minute evaluation in 2026 typically costs $250 to $500.
- Maintenance Checks: Follow-up “medication management” visits (15–30 minutes) usually range from $100 to $250.
- The Gap Solution: High-quality telehealth platforms often offer flat-rate psychiatric follow-ups for $80 to $150, making them a more predictable option for the uninsured.
Mandatory Lab Monitoring Costs
If you are prescribed Lithium or certain anticonvulsants, blood work is not optional.
- Lithium Serum Levels: To prevent toxicity, you need blood draws. Independent labs like Quest or LabCorp offer “patient-initiated” pricing, which can lower a $200 hospital lab bill to $45–$60.
- Metabolic Screening: Antipsychotic medications often require checking your blood sugar and cholesterol annually, costing roughly $30–$80 out-of-pocket.
2026 Medication Price Guide (Cash Pay)
The cost of your prescription depends entirely on whether the drug has a generic equivalent.
The “Affordability” Tier (Generics)
Using discount cards like GoodRx, SingleCare, or Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drugs, these prices represent the typical 30-day “cash” cost:
- Lithium Carbonate: $12 – $25
- Lamotrigine (Generic Lamictal): $8 – $30
- Quetiapine (Generic Seroquel): $9 – $40
- Aripiprazole (Generic Abilify): $11 – $45
- Lurasidone (Generic Latuda): $17 – $55
The “Access Needed” Tier (Brand Names)
For newer medications with no generic version, the prices can be prohibitive without intervention:
- Vraylar (Cariprazine): $1,200 – $1,400+
- Caplyta (Lumateperone): $1,300 – $1,500+
- The Access Key: If these are required, you must bypass the pharmacy counter and apply for Patient Assistance Programs (PAPs) directly through manufacturers like AbbVie or Otsuka.
Therapy Without Insurance: Strategies for Lowering Costs
Talk therapy is a critical secondary pillar for bipolar stability. While private-pay rates average $100 to $250 per hour, these alternatives provide high-quality care at a lower entry point:
- Sliding Scale Clinics: Nonprofits often use a “pay what you can” model based on your income.
- Open Path Collective: For a small lifetime fee, this nonprofit connects you with therapists who charge between $40 and $70 per session.
- University Training Centers: Supervised graduate students at local universities, who often provide sessions for $10 to $25.
The “Safety Net” Hierarchy: Where to Get Help Now

If you are facing a financial wall, follow this step-by-step path to secure treatment:
Level 1: Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs)
These are government-funded clinics (like Signature Health or Project Renewal) that specialize in treating the uninsured. They use a sliding-fee scale and often have in-house pharmacies with 340B pricing, which can reduce medication costs to nearly zero.
Level 2: Nonprofit Grant Foundations
Organizations like the PAN Foundation provide specific “Bipolar Disorder Copay Grants.” Even if you are uninsured, they can sometimes offer “Premium Assistance” or direct grants to help you afford the care you need.
Level 3: The 48-Hour Early Intervention Rule
The most effective way to save money is to prevent a crisis. An emergency room visit or psychiatric hospitalization can cost $1,500+ per day. By seeing a $150 sliding-scale psychiatrist the moment you feel a mood shift (within 48 hours), you avoid the massive financial burden of inpatient care.
Cost Comparison Tables: 2026 Price Snapshot
Medication Price Tiers (Generic vs. Brand)
| Medication | Est. Generic Monthly (with Coupon) | Est. Brand Monthly (Cash Price) |
| Lithium | $12 – $18 | $900+ (Lithobid) |
| Quetiapine | $7 – $30 | $600+ (Seroquel) |
| Lamotrigine | $7 – $25 | $500+ (Lamictal) |
| Aripiprazole | $11 – $40 | $950+ (Abilify) |
| Lurasidone | $17 – $55 | $1,400+ (Latuda) |
Out-of-Pocket Diagnostic Costs
| Test / Service | Estimated Cash Price | Frequency |
| Lithium Serum Level | $45 – $150 | Every 3–6 months |
| Thyroid Panel (TSH) | $30 – $80 | Annually |
| Metabolic Panel | $25 – $70 | Biannually (for Antipsychotics) |
Frequently Asked Questions
How much is bipolar medication without insurance?
On average, generic mood stabilizers and antipsychotics cost between $15 and $60 per month when using discount cards like GoodRx or SingleCare. Brand-name medications like Vraylar or Caplyta can cost between $1,200 and $1,600 per month if paid in cash, though patient assistance programs can often bring this to $0 for eligible individuals.
How much does it cost to treat bipolar disorder?
A standard year of outpatient care for an uninsured patient typically ranges from $2,500 to $5,000. This estimate includes one initial evaluation ($400), six follow-ups ($1,200), monthly medications ($400), and bi-weekly therapy sessions ($2,400).
How to get treatment for bipolar disorder without insurance?
Search for Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) or Community Mental Health Centers via the HRSA website. These facilities receive federal grants to provide care on a sliding-scale basis, often allowing you to see a psychiatrist for under $50 based on your income.
How much is lithium medication?
Generic Lithium Carbonate is one of the most affordable psychiatric drugs, often retailing for $15 to $25 for a 30-day supply. However, factor in the $45–$150 cost of periodic blood tests required to monitor lithium levels and kidney function.
How much is lamotrigine without insurance?
Generic lamotrigine (Lamictal) typically costs $10 to $35 per month, depending on the dose (100mg vs. 200mg). Prices are often significantly lower at warehouse clubs like Costco or through mail-order pharmacies like Amazon Pharmacy or Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drugs. Conclusion
While the financial burden of a chronic mental health condition is undeniable, a lack of insurance does not have to be a dead end for your recovery. In 2026, the combination of a robust generic drug market, the expansion of telehealth platforms, and the legal requirement for sliding-scale fees at community clinics has created a viable path for everyone to access care.
The key to financial survival with bipolar disorder is proactive planning. By identifying your local FQHC, keeping a list of your generic medication options, and honoring the 48-hour rule to prevent hospitalization, you can manage your symptoms without compromising your financial future.
Managing bipolar disorder is an investment in your life. While the costs are real, the cost of an untreated illness—in terms of lost income, strained relationships, and physical health—is always far higher. You are worth the effort it takes to find affordable care.
Authoritative References
- National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH):Mental Health Medications
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI):Managing Bipolar Disorder
- Mayo Clinic: Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis and Treatment
- Treatment Advocacy Center (TAC): Severe Mental Illness Resources
- PAN Foundation: Bipolar Disorder Fund
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get mental health tips, updates, and resources delivered to your inbox.